MCP 入门指南
MCP,全称 Model Context Protocol,由 Anthropic 在 2024 年 11 月推出的,社区共建的开放协议。目的是提供一个通用的开放标准,用来连接 [[LLM]] 和外部数据、行为。
近段时间,LLM 表现出强大的学习能力和规划能力,能够处理更加复杂、抽象的任务。这种强大的能力,让我们看到了 LLM 在 AGI(通用人工智能)中的巨大潜力。但同时,LLM 也不是万能的,它缺失了很多能力。LLM 可以作为[[智能体]]的大脑,外部工具就是智能体的手和脚,协助智能体执行决策。
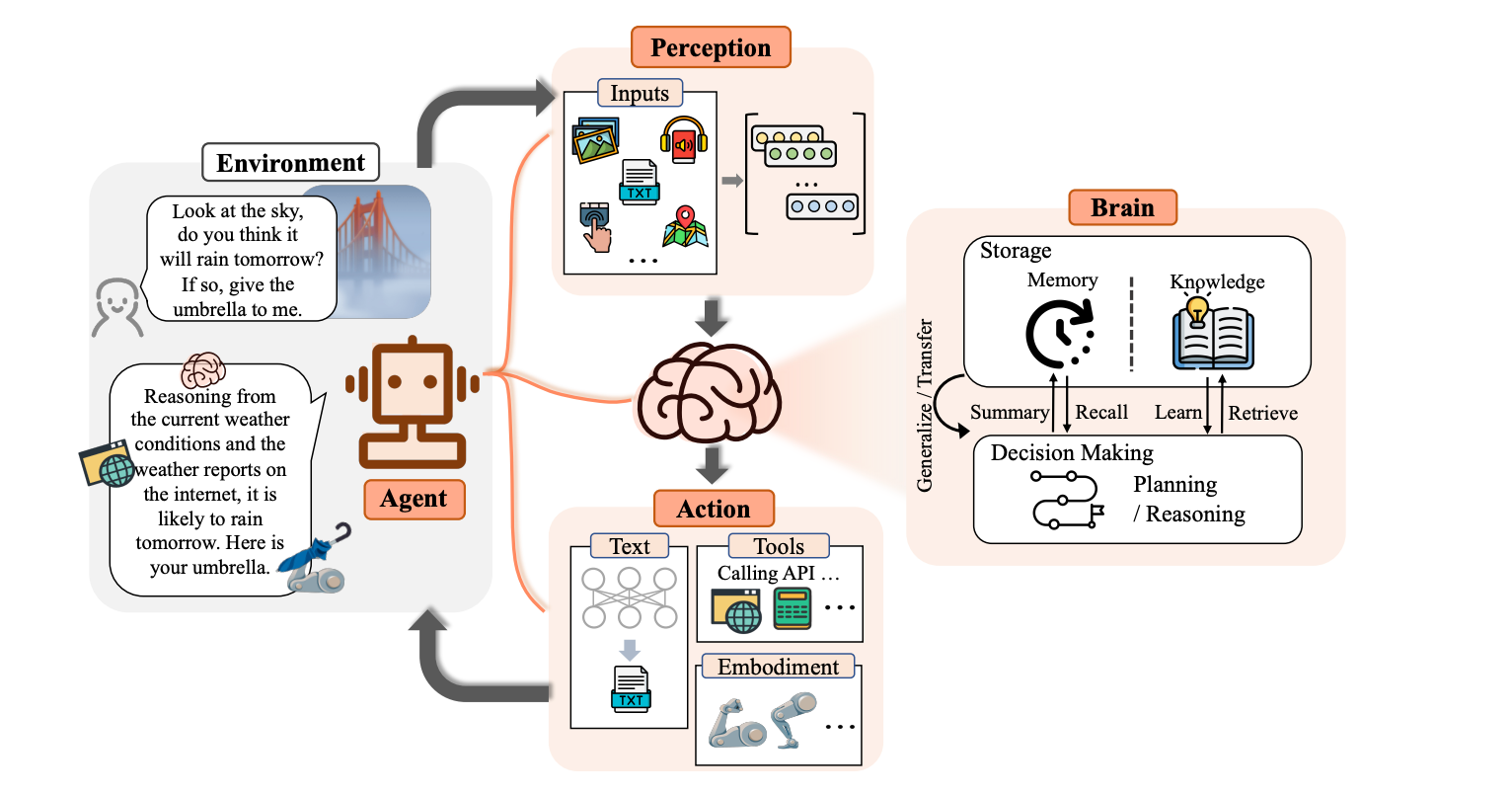
一个典型的 Agent 的设计,LLM 充当大脑模块,通过多模态输入,处理信息,然后做出决策和规划行动。
MCP 就是想要通过一个开放的协议,为外部工具(或数据源)提供统一和 LLM 交互的统一集成。
MCP 就是手脚连接身体的“关节”。
MCP 的系统架构如下:
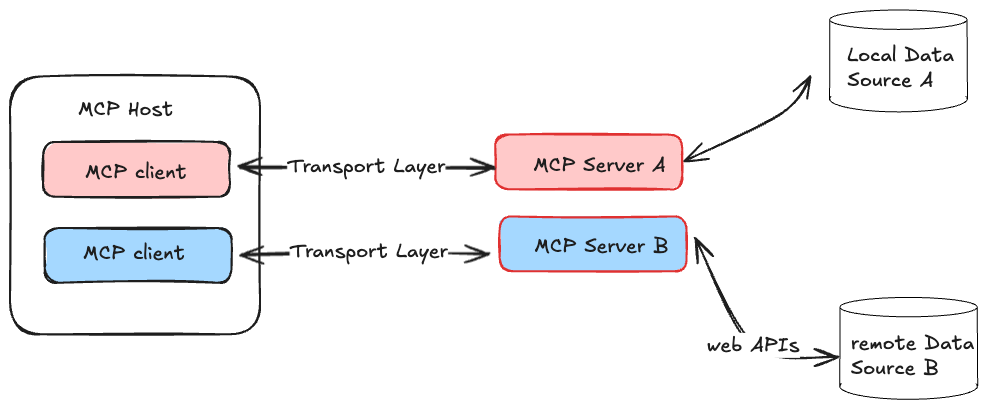
主要有以下几个概念:
- MCP Host:LLM 的宿主应用,比如 Cursor、Cline 等等,是处理一个或多个 MCP Server 的应用程序。
- MCP Client:Host 内部专门用于与 MCP Server 建立和维持一对一连接的模块。它负责按照 MCP 协议的规范发送请求、接收响应和处理数据。简单来说,MCP Client 是 Host 内部处理 RPC 通信的“代理”,专注于与一个 MCP Server 进行标准化的数据、工具或 prompt 的交换。
- MCP Server:提供外部能力或数据的工具,比如实时获取天气、浏览网页等等能力
MCP Client 更多是一个底层技术术语,是关于 MCP Server 连接到 MCP Host 的底层细节,不用过于区分 MCP Host 和 MCP Client。
MCP 的可能性#
MCP 当前的发展还处在非常早期的阶段,尤其是其他 LLM 大厂,比如 OpenAI、Google 会不会跟进规范也不确定,社区目前也并不活跃。但它仍然存在一定潜力:
- 提供了简化 Agent 开发的方案
- 相对而言,MCP 不依赖任何特定的 LLM
- MCP Server 可被扩展,可被复制,可被重用
- MCP 协议中增加了安全性的控制
MCP Server 的下载安装#
目前有很多客户端已经支持 MCP Servers 的使用,比如 Cline、Cursor,可以直接在这些客户端中使用社区开发好的 Servers。下面是一些收集 MCP Servers 的网站:
由于 MCP Servers 通常是由官方提供的 TypeScript SDK 或 Python SDK 构建的,因此需要在电脑上安装:
比如,我们需要安装 fetch 这个 Server 来支持 Agent 提取 web 内容。配置如下:
"mcpServers": {
"fetch": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["mcp-server-fetch"]
}
}
在 Cursor 中,可以这样配置:
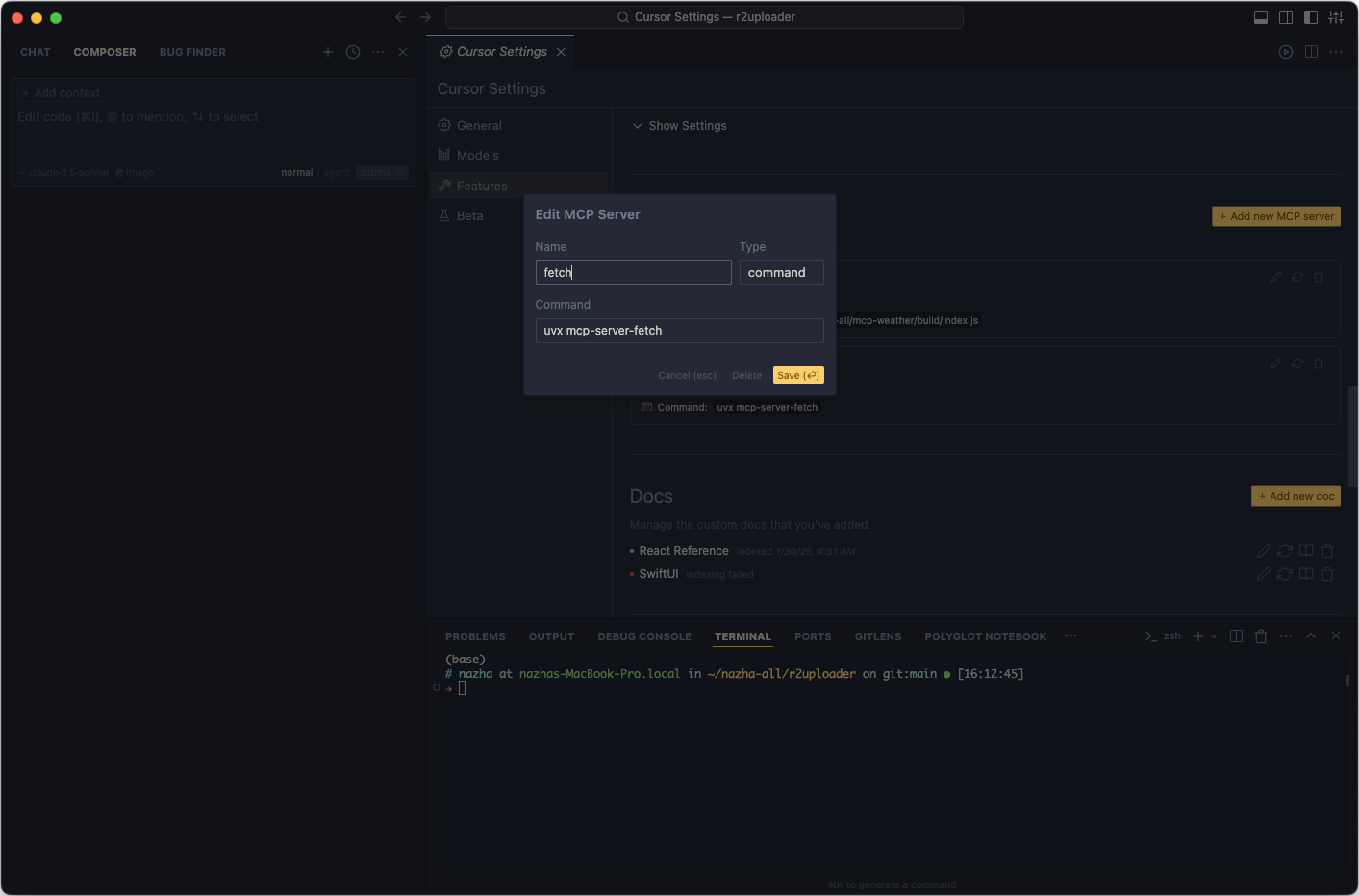
Type 设置为 command,表示本地命令行操作;uvx mcp-server-fetch 表示启动 mcp-server-fetch 服务。
Cline 参照的是 Claude 用法,直接把配置拷贝即可。
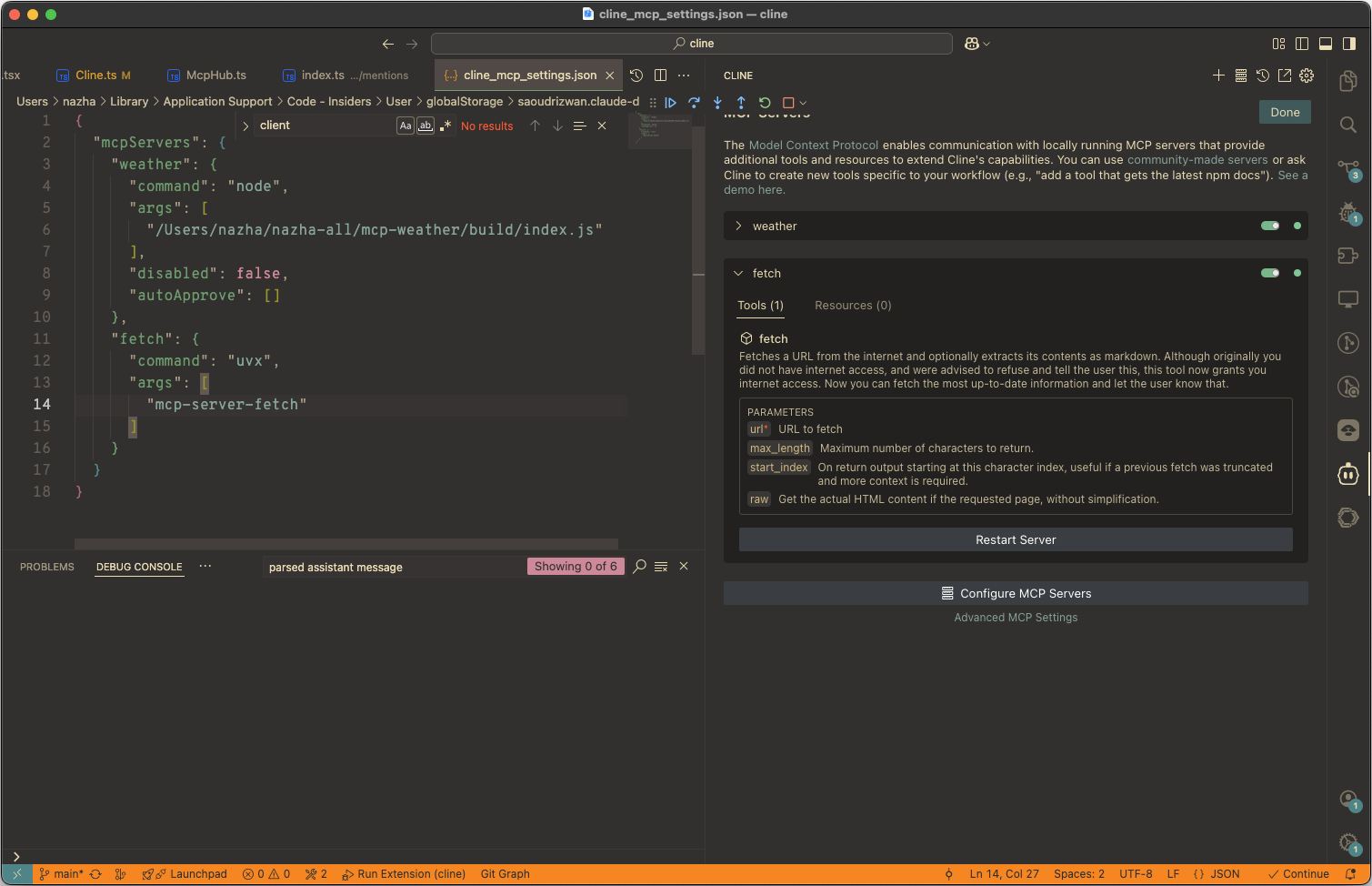
MCP 标准协议中存在一个握手过程,用来验证 Server 是否正常(图中绿色的小点代表握手成功)。
这样,你的 Chatbot 就拥有了爬取网页的能力。那如何唤起这个能力呢?
MCP Server 的使用#
在使用中,通常有两种方式来触发 MCP Server 的调用(都是通过 prompt 调用,也叫作 prompt tool use)。
- 通过 Server 的名称或描述,显式调用
比如:fetch this post https://www.nazha.co/posts/how-cline-works, and summarize it. 其中,fetch 就是关键词。
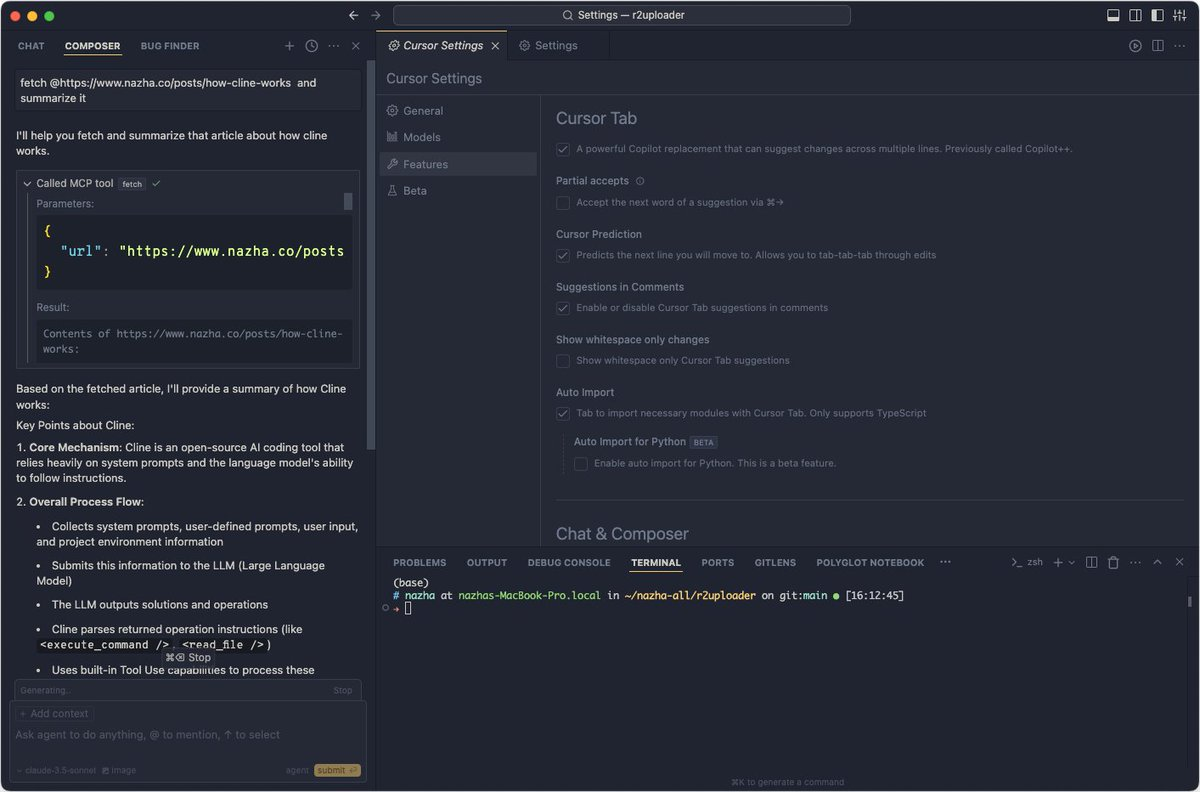
- 让 Agent 自己确定使用哪些工具
只描述需求,让 LLM 自己来确定是否要使用到某些工具。
常见的有用、好玩的 Server#
下面推荐介绍一些好用、好玩的 Server :
- Brave Search - 让 Agent 加上搜索的翅膀
用来进行网络搜索,即 brave_web_search 和 brave_local_search。借助 Brave 提供的能力。配置如下:
"mcpServers": {
"brave-search": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"-y",
"@modelcontextprotocol/server-brave-search"
],
"env": {
"BRAVE_API_KEY": "YOUR_API_KEY_HERE"
}
}
}
在使用前,需要申请 Brave Api Key。
用来读取网页内容。也可以配合 Brave Search 来使用。配置如下:
"mcpServers": {
"fetch": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": [
"mcp-server-fetch"
]
}
}
比如这个例子:search Sam Altman,and get the latest post of Sam Altman
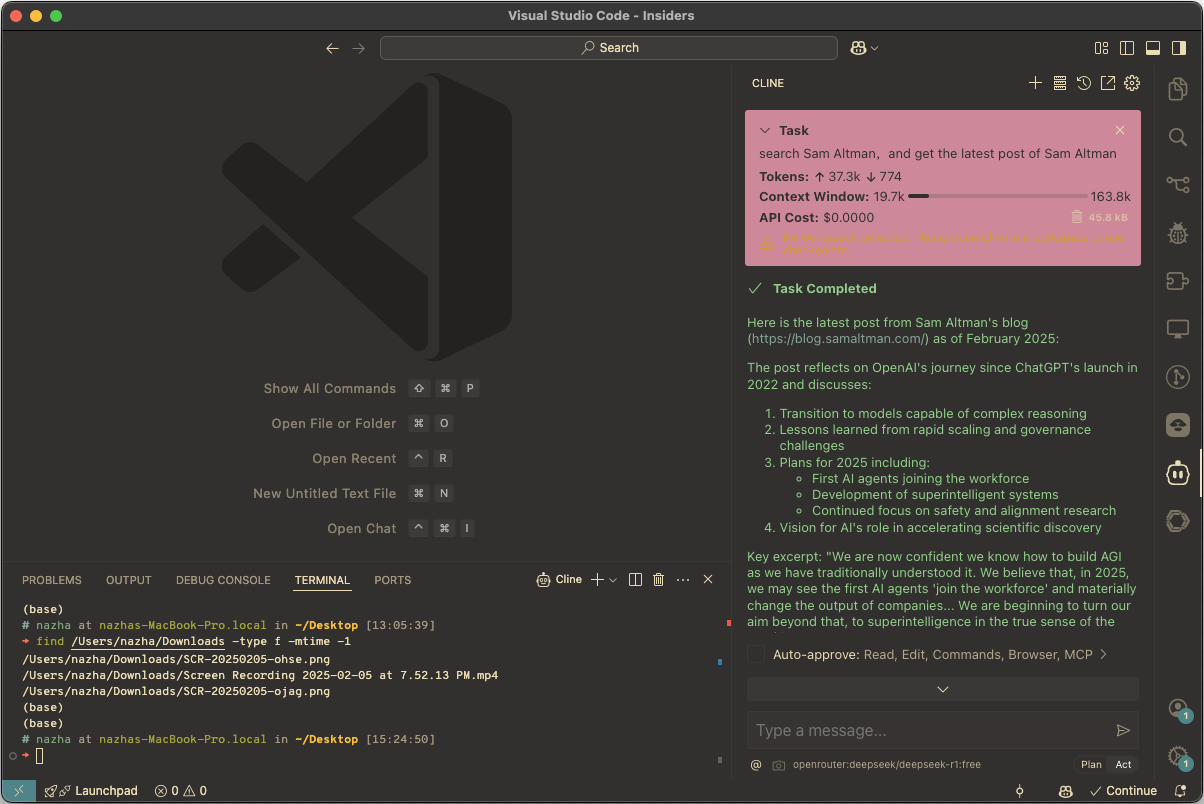
Agent 先通过 Brave Search 搜索 Sam Altman,然后用 fetch 读取其博客的内容,分析结果得到其最新的博客文章是:Reflections,就这样实现了 LLM 的连网能力。
- puppeteer - 增强 Agent 的自动化
Puppeteer 可以支持浏览器自动化,当前 @modelcontextprotocol/server-puppeteer 列出的一些能力有:
puppeteer_navigate- 页面跳转puppeteer_screenshot- 截屏puppeteer_click- 元素点击puppeteer_hover- 元素 Hoverpuppeteer_fill- 文本填空puppeteer_select- 选中选择框的元素puppeteer_evaluate- 在 Console 中执行 JavaScript 代码
依托这个 MCP Server,可能可以做一些自动化的操作,比如 UI 自动测试、爬虫一类的事情。
配置如下:
"mcpServers": {
"puppeteer": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"-y",
"@modelcontextprotocol/server-puppeteer"
]
}
}
这个 Server 可以用来读取和搜索 Obsidian Vault 中的内容。
- 其他服务集成
各类服务也可以接入 MCP 提供能力,比如:
- 如果想要接入 [[RAG]],Needle 这个 SaSS 服务支持了 MCP。
- 支持图像能力,可以接入 Replicate 这个服务,使用 mcp-server-replicate 这个 Server。
MCP 的背后 - 跟 LLM 的集成#
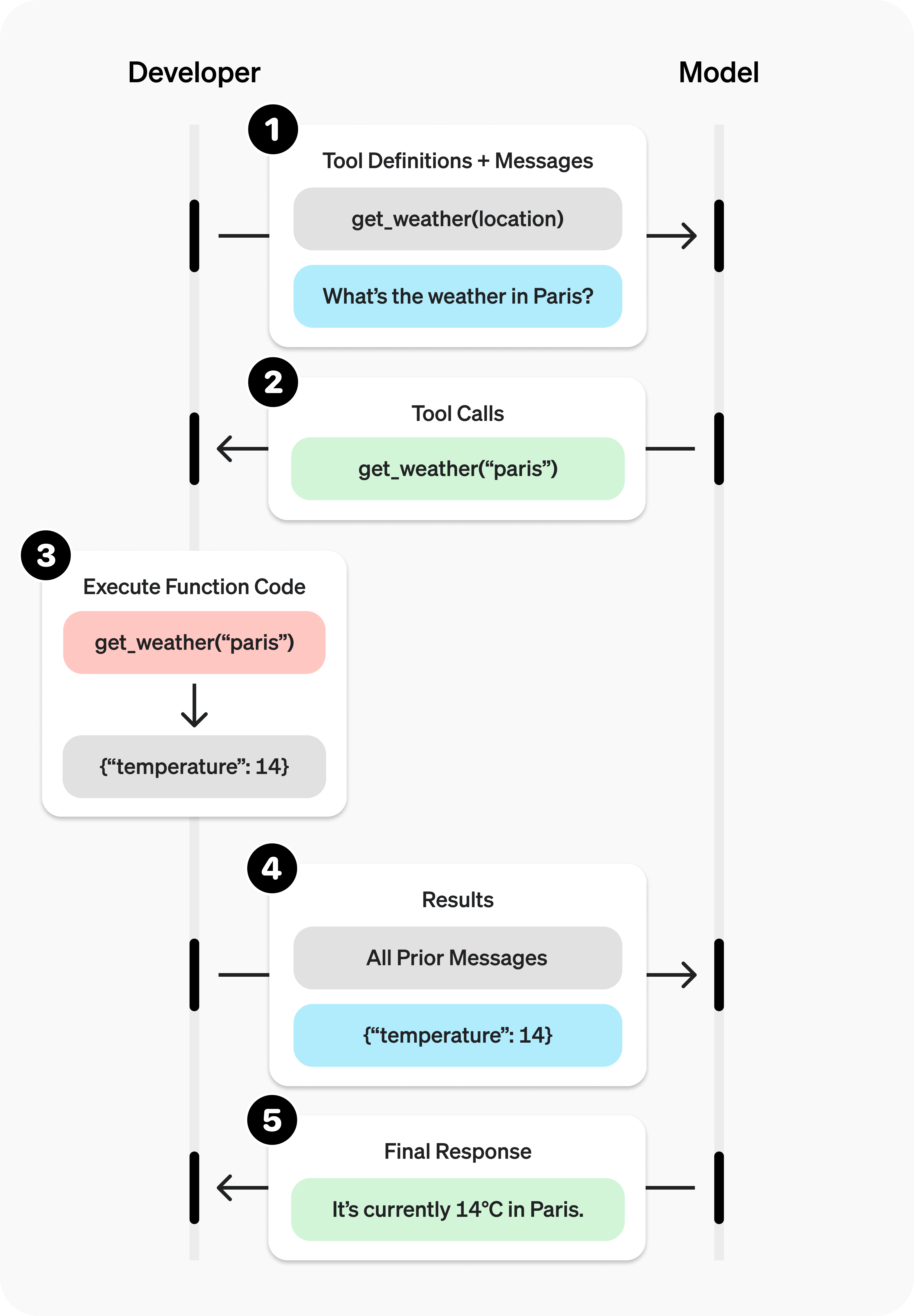
LLM 为什么能够使用这些工具,其背后是一个典型的 Agent 实现方式。它是一个多步的操作:
- 给 LLM 发送初始 prompt
- 等待 LLM 给出 MCP Server 使用的响应
- 客户端调用 MCP Server 的工具使用函数
- 调用结果返回,并把结果再次提供给 LLM
LLM 访问可使用的工具#
目前让 LLM 识别有哪些可用的工具的思路有以下两种:
- 通过支持 Tool Use 的官方接口,比如 Anthropic 的 Tool Use 接口 和 OpenAI 的 Function Calling 接口。
以 Anthropic 的接口为例:
import { StdioClientTransport } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/client/stdio.js"
const tools = await mcpClient.request({
// 获取 tools 列表
method: "tools/list"
}, ListToolsResultSchema);
const response = await this.anthropicClient.messages.create({
messages: [
{
role: 'user',
content: 'What is the weather in Shanghai',
},
],
model: 'claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022',
max_tokens: 8192,
tools: this.tools, // 传递 tools
});
以 OpenAI 的接口为例:
import { StdioClientTransport } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/client/stdio.js"
const tools = await mcpClient.request({
// 获取 tools 列表
method: "tools/list"
}, ListToolsResultSchema);
const compatibleToolFuncForOpenAI = (tools?.tools ?? []).map(tool => ({
type: 'function',
function: {
name: tool.name,
description: tool.description,
parameters: tool.inputSchema,
},
}))
let completion = await openai.chat.completions.create({
model: 'gpt-4o-mini',
store: true,
tools: compatibleTools,
messages: [{
role: 'user',
content: 'What is the weather in Shanghai'
}],
});
- 通过系统 Prompt,依赖 LLM 的指令遵循
方案一不具备通用性,受限于 LLM 服务商提供的能力。为了让其他 LLM 也拥有 Tool Use 的能力,可以通过上下文学习的方式微调 LLM。通常来说,LLM 有很强的指令遵循的能力,在训练过程中也涌现出工具使用的能力。
比如下面的一个系统 system prompt 的例子(源 prompt 参考 cline system prompt)
export const getSystemPrompt = (tools) => `TOOL USE
You have access to a set of tools that are executed upon the user's approval. You can use one tool per message, and will receive the result of that tool use in the user's response. You use tools step-by-step to accomplish a given task, with each tool use informed by the result of the previous tool use.
# Tool Use Formatting
Tool use is formatted using XML-style tags. The tool name is enclosed in opening and closing tags, and each parameter is similarly enclosed within its own set of tags. Here's the structure:
<tool*name>
<parameter1_name>value1</parameter1_name>
<parameter2_name>value2</parameter2_name>
...
</tool_name>
For example:
<use_mcp_tool>
<server_name>weather-server</server_name>
<tool_name>get_forecast</tool_name>
<arguments>
{
\"city\": \"San Francisco\",
\"days\": 5
}
</arguments>
</use_mcp_tool>
Always adhere to this format for the tool use to ensure proper parsing and execution.
# Tools
# Tool Use Examples
## Example 1: Requesting to use an MCP tool
<use_mcp_tool>
<server_name>weather-server</server_name>
<tool_name>get_forecast</tool_name>
<arguments>
{
\"city\": \"San Francisco\",
\"days\": 5
}
</arguments>
</use_mcp_tool>
====
MCP SERVERS
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) enables communication between the system and locally running MCP servers that provide additional tools and resources to extend your capabilities.
# Connected MCP Servers
When a server is connected, you can use the server's tools via the \`use_mcp_tool\` tool, and access the server's resources via the \`access_mcp_resource\` tool.
## weather (\`node /Users/nazha/nazha-all/mcp-weather/build/index.js\`)
### Available Tools
${tools.map(tool => `- ${tool.name}: ${tool.description}\nInput Schema: ${JSON.stringify(tool.inputSchema)}`).join('\n')}
# MCP Servers Are Not Always Necessary
The user may not always request the use or creation of MCP servers. Instead, they might provide tasks that can be completed with existing tools. While using the MCP SDK to extend your capabilities can be useful, it's important to understand that this is just one specialized type of task you can accomplish. You should only implement MCP servers when the user explicitly requests it (e.g., \"add a tool that...\").
Remember: The MCP documentation and example provided above are to help you understand and work with existing MCP servers or create new ones when requested by the user. You already have access to tools and capabilities that can be used to accomplish a wide range of tasks
====
`
LLM 的输出结果可能是:
I can get the weather forecast for San Francisco. Please hold on for a moment while I retrieve that information.
I'll use the location's latitude and longitude to get the forecast. San Francisco's coordinates are approximately 37.7749° N, 122.4194° W.
Let me get the forecast for you.
<use_mcp_tool>
<server_name>weather-server</server_name>
<tool_name>get-forecast</tool_name>
<arguments>
{
"latitude": 37.7749,
"longitude": -122.4194
}
</arguments>
</use_mcp_tool>在 Cline 的 system prompt 中,约定了可使用的 MCP Server 及其能力。通过解析 LLM 返回约定指令,调用 MCP Server。
MCP 工具调用#
在获取 LLM 调用指令之后,即可调用 MCP Server 来获取结果返回:
// Wait for the LLM to respond with a tool use
if (content.type === 'tool_use') {
const toolName = content.name;
const toolArgs = content.input;
// Call the tool handler on the MCP Server
const toolResult = await mcpClient.request(
{
method: 'tools/call',
params: {
name: toolName,
arguments: toolArgs,
},
},
CallToolResultSchema,
);
获取到 MCP Server 返回结果后,再次作为上下文提交给 LLM 处理。
const completion = await openai.chat.completions.create({
model: 'gpt-4o-mini',
store: true,
messages: [{ role: 'user', content: prompt }, { role: 'user', content: toolResponse.content?.[0]?.text }],
});
这样 Agent 的一轮交互就结束了。
更多有关 LLM 集成的工程化考量,推荐大家阅读 MCP Client Development Guide: Building Robust and Flexible LLM Integrations
MCP Server 的能力#
MCP Server 目前支持三类可被复用的能力:
- Tools
最常见的能力,向 LLM 提供可执行的功能,比如爬取网页内容、获取天气信息等,可以用来让 LLM 跟外界系统进行交互。
- Resources
允许 LLM 公开读取 Server 的数据或内容的能力。比如, puppeteer 这个 Server 就提供了对外读取浏览器控制台输出的能力。一般来说,也可以由 Tools 替代,但语义上对 LLM 更友好。
- Prompts
这个能力支持提示词的共享。
MCP Server 的开发也比较简单,官网 也提供了示例参考。
小结#
MCP 任重而道远。